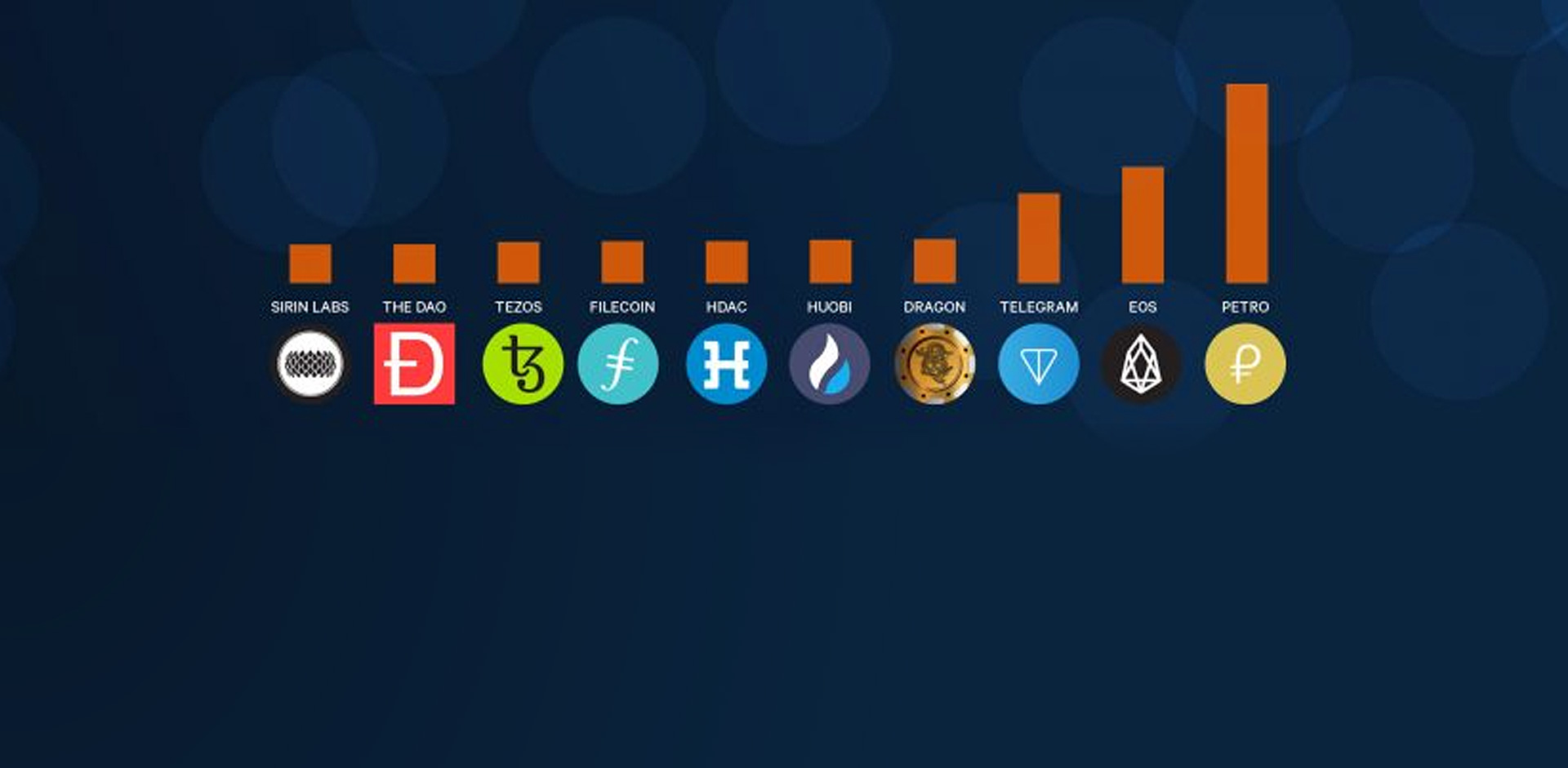
TOP 10 biggest ICO Crypto
2017 has been the breakout year for blockchain-focused startups. With massive gains on the top 100 cryptocurrencies, early investors within the community are re-investing in projects of all kinds.
Table of Contents
EOS
The blockchain startup Block.one launched the ICO for its EOS platform in June 2017 and concluded the token sale in June 2018. During the token sale period, EOS managed to raise $4.1 billion to fund the development of its next-level scalable smart contracts platform. EOS is considered by some to be the “Ethereum of China” and has attracted a substantial amount of its investments from individuals based in the People’s Republic.
Why This Worked
EOS is developing a scalable smart contracts platform that has the potential to become a “better” Ethereum, as the Ethereum network suffers from severe congestion issues at times. Scalability is very important for mass adoption of a blockchain network. Hence, EOS is well-positioned to become a major blockchain and smart contract platform in the future.
Telegram
The company behind the popular end-to-end encrypted messaging app Telegram managed to raise $1.7 billion during a private sale involving SAFT agreements, which led to the company scrapping its public sale. The money raised in the token sale is said to go toward developing the Telegram Open Network (TON), which will be supported by its proprietary digital token called GRAM.
Telegram’s planned blockchain network aims to solve the issue of scalability by building an entirely new blockchain that can process millions of transactions per second through the use of “infinite sharding” and “hypercube routing”.
Why This Worked
For venture capital firms and hedge funds who are new to the world of cryptographic assets, Telegram was an “easy” first investment as the token will be issued by a large reputable company. However, since the Telegram Open Network makes a lot of promises that are technologically challenging, many experienced cryptocurrency investors have passed on this private token sale.
Dragon
The Dragon ICO stood out from its peers as it is the first token sale that was conducted to fund a floating casino in Asia’s gambling haven Macau. During its token sale, Dragon Corp managed to raise an impressive $320 million (out of the $500 target) for its gambling venture.
The Dragon Coin, DRG, is a digital currency targeted at VIP gamblers in Macau and its value is driven by the success of a large gambling venture.
Why This Worked
Despite its rumored association with a Macau-based gangster and its business relationship with Cambridge Analytica, Dragon has managed to become one of the most successful ICOs in history.
Through the use of its digital currency Dragon Coin, Dragon wants to help high rollers save money by disintermediating money transfer agents who take a substantial fee when international gamblers convert money in their local currency into money that can be used to gamble in Macau.
Huobi
China-based Huobi, one of the largest cryptocurrency exchanges in the world, decided to follow in the footsteps of other exchanges that managed to raise billions by selling a native digital token and raised $300 million through its highly publicized token sale in early 2018.
The exchange sold its HT token to its existing users who can benefit from the discount on trading fees on the exchange.
Why This Worked
As the success of Binance Coin shows, exchange-issued tokens that provide users with a discount on trading fees are attractive to cryptocurrency investors. Huobi jumped on this bandwagon and managed to cash in.
Hdac
South Korean technology company Hdac managed to raise $258 million in late 2017 to fund the development of “the world’s 1st IoT contract & payment platform based on Blockchain”. The Hyundai BS&C-backed company aims to enable IoT devices to communicate, handle identity authentication, data storage, and payments.
Hdac plans to achieve this by developing a new blockchain that will handle the scaling and contract functionality required for an IoT platform as well as a bridge to digital currencies to facilitate payments.
Why This Worked
Hdac benefited from strong publicity in South Korea as well as backing from one of Korea’s leading car manufacturers, which helped to legitimize the venture. Furthermore, Hdac aims to provide blockchain-based IoT solutions, which is not a difficult sell on the back of the success of Hdac’s biggest competitor IOTA.
Filecoin
The Filecoin ICO has raised over $257 million during its September 2017 token offering after already having raised $52 million from leading venture capital firms such as Union Square Ventures, Andreessen Horowitz, and the Digital Currency Group prior to the token sale. Filecoin aims to build a decentralized cloud storage network using the InterPlanetary File System (IPFS) to securely record and store data on a peer-to-peer basis.
This ICO stands out since it complies with the new SEC regulations on ICOs, only allowing accredited investors to partake in its token sale.
Why This Worked
Not only was Filecoin the first regulatory-compliant initial coin offering in the U.S., the project also offers a top-tier technological solution for a growing market. Furthermore, the project has received financial backing from several of the world’s leading blockchain venture capital investors ahead of the ICO, giving the project the needed stamp of approval to raise the staggering amount it was able to secure during its token sale.
Tezos
The Tezos project raised over $232 million during its ICO in July 2017. The Tezos team is developing a self-amending distributed ledger that allows for the creation of smart contracts. Tezos stands out from other blockchain projects since it allows token holders to approve and fund new protocol updates and, therefore, pre-emptively mitigate scaling or development disputes that may arise for the network in the future.
Tezos’ token, called Tez (XTZ), will become tradable on digital currency exchanges in the coming months.
Why This Worked
The Tezos project is addressing pressing issues in the cryptocurrency community, which are governance and the decision-making process in relation to blockchain technology. The team behind the Tezos project has been developing a blockchain that enables its token holders to become the decision makers when it comes to important protocol updates and thereby democratizes the governance of its blockchain.
Ironically, the founders of Tezos became embroiled in a legal dispute with the director of the Tezos Foundation to access the ICO funds to continue the development of their platform. The issue was eventually resolved and Tezos investors can now trade their XTZ tokens on exchanges.
Sirin Labs
The Swiss blockchain venture Sirin Labs managed to raise $157.8 million during its token sale in December 2017 to fund its vision of becoming “the world’s leader in secure open source consumer electronics, bridging the gap between the mass market and the blockchain economy.” More specifically, the funds raised during the crowdsale will support the development of FINNEY™, the first open source blockchain smartphone and all-in-one PC.
Why This Worked
The demand for secure PC and smartphone solutions is increasing as fraud and cybercrime are becoming a growing threat to consumers. Hence, the appeal of a blockchain-secured computing device is very high.
Bancor
The blockchain-based prediction market project Bancor held its ICO on June 12, 2017, where it managed to raise $153 million worth of Ether for the development of its platform. Investors in the crowdsale also included VC firm Blockchain Capital as well as seasoned blockchain investor Tim Draper.
The Bancor (BNT) token experienced a spike on the day it launched on exchanges to hit a high of $4.49 and then dropped off to trade at a low of $1.49. In late August, the BNT token recovered and surpassed the $3.00 mark again. Today, the BNT token is trading at $2.25.
Why This Worked
Bancor is a protocol that allows anyone to issue new cryptocurrencies called ‘smart tokens’ that can be easily exchanged against reserve tokens, which alleviate the issues surrounding liquidity and price discovery for newly issued tokens. As the demand for digital currencies rises, the need for an easy-to-use issuance and trading platform increases too. That is where the Bancor protocol comes into the picture.
The DAO
The fifth largest ICO to date was also one of the most controversial. The token sale for the DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization) raised $152 million worth of Ether in May 2016 to a create a decentralized investor-driven venture capital fund that would invest in promising new projects built on the Ethereum blockchain. The controversy around the DAO started a month after the crowdsale when it was discovered that a vulnerability in the DAO’s smart contract allowed a hacker to steal around one-third of the invested Ether.
What became known as “the DAO hack” later led to the dissolution of the DAO and a hard fork in the Ethereum blockchain that allowed Ether holders to restore their Ether holdings back to prior to the hack. The DAO hack also caught the eye of the SEC, which announced in July that the sale of the DAO tokens would have been considered as the issuance of securities and should, therefore, have been subject to regulation. This statement initiated new ICO regulations that are currently being put in place in the US.
Why This Worked
Despite the DAO’s abrupt downfall, this initial coin offering was able to raise such a large amount of money since the project – in theory – allowed investors to gain exposure to blockchain projects in a decentralized manner. In other words, it was one of the very few ways to gain investment exposure to various blockchain projects without having to invest in each individually, which was rather revolutionary at the time.
Also, the DAO focused on a highly active community, the Ethereum community, which helped the project gain so much traction in such a short period of time.





